If you are considering to invest in solar, the following will explain the process to ensure you get the optimum solution for your business.
Did you know that the return on investment for commercial solar is often between 25% to 33% per year, it’s one of the best investments around.
Evaluating a commercial electricty account is not easy.
Following is an explanation of how to identify the true cost per kWh of electricty and the other associated costs that you will find on a commercial electiricty account.
Firstly, let’s gain an understanding of the various charges and key information that you will find on most accounts.
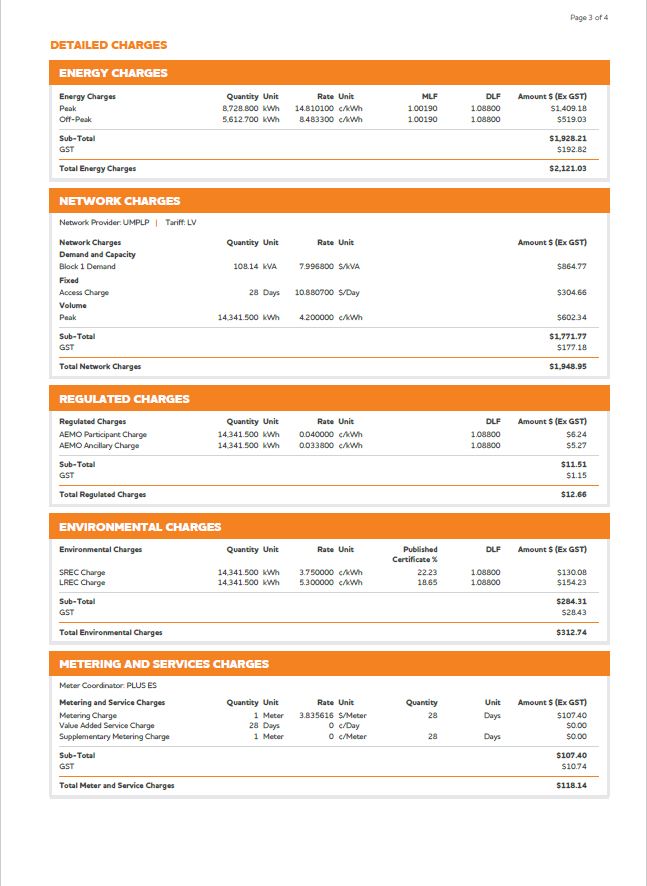
Period – you need to know how many days of electricity use the bill relates to. The bill to the right is for 28 days.
Energy Charges – Electricty is charge in units of kilo Watt hours (kWh) consumed during the Period and typically you these will be seperated into various rates depending on the time of consumption.
Peak – This is the amount of kWh’s used xxam and xxpm on Monday to Friday each week
Off Perk – This is the amount of kWh’s used between xxpm and xxam Monday to Friday and on the weekends.
Shoulder – Some bills will also have a seperate rate for the Shoulder, this is typcially for kWh’s consumed between 12 noon to 4pm Monday to Friday.
Network Charges – Network Charges are fees that are charged by the network operator to pay for the infrusture required to transmit energy from the electricity generators to the consumers. These fees are broken into the following catagories.
Demand Charges – Demand Charges are charged in units of kVA. (As the kVA demand increases at a particular business site, the electricity infrustracture to ensure reliable energy to the site increases in its scales and capacity.)
Daily Access Fee – This is a fixed fee that is charged for each day include in the bill Period.
Volume – This fee relates to the total comsumption of electrictiy at the site and is charged per kWh unit delivered during the period.
Regulatory Charges – These charges relate to cost imposed under government legislation and go to the governement to pay for various programs.
AEMO Particatant Charge –
AEMO Ancillary Charge –
Environment Charges
Installation and Commissioning
<30kw, <100kW, >100kW
Applications and Approvals
Installation
Commissioning
Monitoring
Cleaning and Maintenance